
Advanced persistent threats refer to the type of attacks in which the perpetrators gain unauthorized access to the target system or network. This type of attack can remain in effect for a long duration without being detected.
Enterprises are at greater risk from this type of attack and hackers can obtain a lot of confidential company data via these attacks. Advanced persistent threats do not damage the local systems or the company network.
Their only goal is to infiltrate the network stealthily to steal sensitive data, intellectual property, takeover a site completely, and sabotage critical organizational infrastructures.
How do Advanced Persistent Threats work?
The Internet can be used to deliver a malicious payload and gain access, or the network may be infected by a physical malware. External exploitation techniques may also be a way to access protected company networks.
Advanced persistent threats are designed in a manner to target a specific enterprise instead of having a generalized purpose. The attack may be executed via a trusted source such as an employee or business partner.
Typically, advanced persistent threats execute their action in a phased manner:
1. Infiltration:
The network is hacked first by exploiting web assets, network resources, or via authorized human users.
2. Expansion
- Remaining obscure,
- Designing the plan of attack,
- Mapping company data to figure out which data is accessible the most,
- Collecting confidential data of the company,
- Monitoring the network activity.
3. Exfiltration
- Exfiltrating that data to the attacker in an undetected manner.
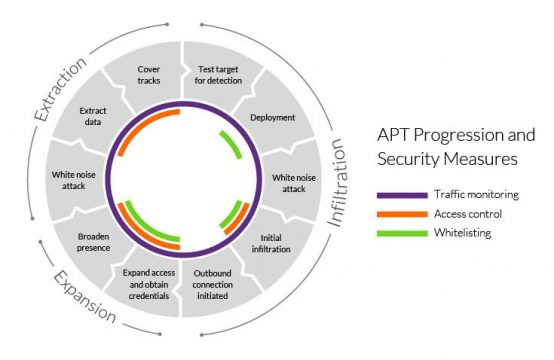
Security measures against APT
Certainly, it is a multi-faceted approach to protect the enterprise network and local systems against APT and consists of a combined effort of network administrators, security providers, and individual users.
- Monitoring the traffic: Monitoring the ingress and egress traffic is the best practice for preventing backdoor installations and thereby, blocking stolen data extraction. Web application firewall and network firewalls should be employed.
- Application and domain whitelisting: Whitelisting apps and domains is a better approach to control what can be accessed rather than blacklisting sites. Strict updated policies are needed to enforce this for the users.
- Access control: Careless users, corrupted insiders, and compromised users are the three main categories of soft-spots that hackers target to launch APT attacks on your organization.
Intruders can be kept at bay by carefully granting user access as per user needs and developing effective controls to review everyone’s access and activities in your organization.
Using two-factor authentication should be enforced at key network access points.
- Additional Measures:
- Patch network software and OS vulnerabilities.
- Encrypt remote connections.
- Filter incoming emails.
- Logging security events immediately.
This is a complete round-about of APT attacks and the security measures that can be undertaken to keep your organization safe.

